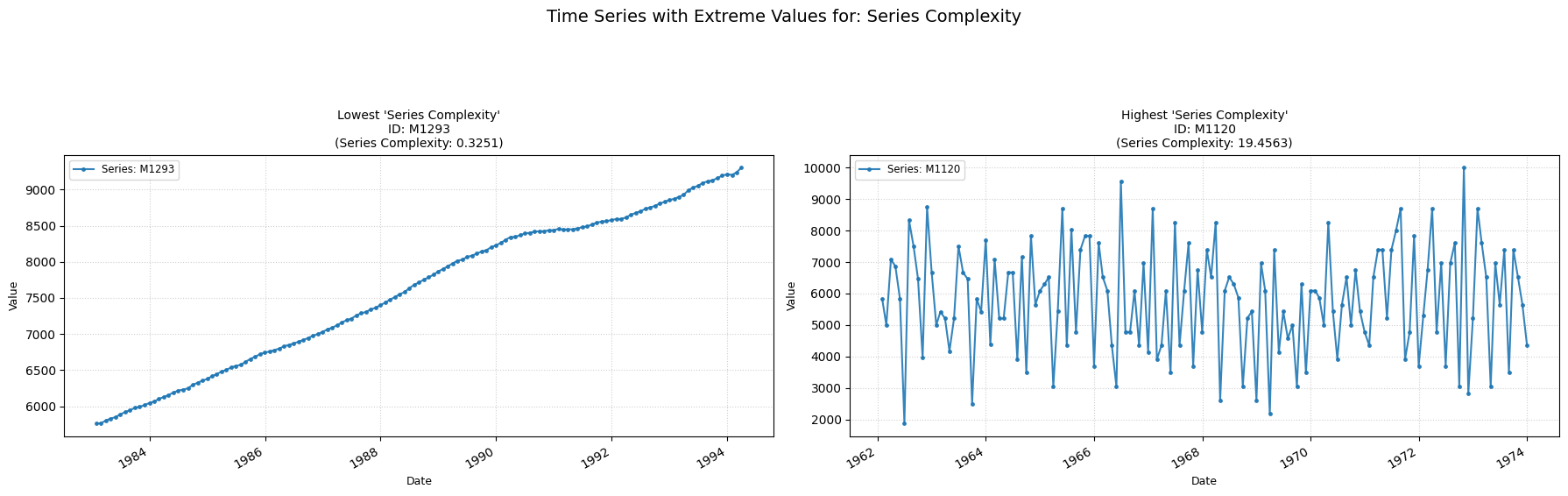
Series Complexity
complexity
Computes the complexity estimate of the z-normalized time series.
Low value: A low/null value means the series is relatively constant over time, with no big changes.
High value: A high value means the series has a high complexity, with several big changes.
No Parameters
Calculation
-
Z-Normalization: First, the series is z-normalized.
-
Raw Complexity Estimate: Then, if the length of Z is less than 2, the returned value for complexity is 0. Otherwise, the complexity of the series is computed in the following fashion:
- The first differences of the normalized series are computed.
- The complexity estimate is computed and returned as the square root of the sum of the squares of these differences.
Practical Usefulness Examples
Signal Processing: When comparing different sensor readings that measure the same phenomenon, a much higher complexity in one signal might indicate noise or interference, rather than true signal variation.
Machine Condition Monitoring: An increase in the complexity of vibration data from a machine over time could indicate developing faults or wear and tear, as the vibrations become less regular.